This section provides examples of various coding combinations for a defined benefit late retirement final average salary benefit.
Refer to Defined benefits under
Product Update Type: Maintain Benefit Rules
Benefit Product (Standard Benefit Rules)
Benefit Product (Flexible Benefit Rules)
For ease of reference, the following standard abbreviations have been used:
- DOE (date of entry)
- NRD (normal retirement date)
- LRD (late retirement date)
In the examples below, it is important to understand that a period of accrual may be from DOE to NRD, from DOE to LRD, or from NRD to LRD. The period of lateness will always be from NRD to LRD, and the increase based on the period of lateness may be applied to any of the three periods of accrual (depending on the rules).
Should the normal retirement age be coded as an age range (rather than a single age), then, for the purposes of the late retirement benefit calculations, NRD will be taken as the retirement date applicable to the last age in the range.

The salary will be averaged at NRD only, and will be applied to the accrual up to NRD (no accrual after NRD).
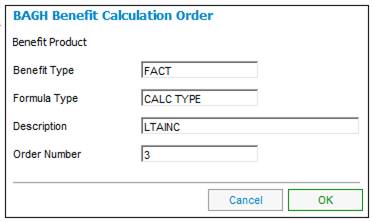
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from DOE to NRD (which, in this example, is the only accrual).
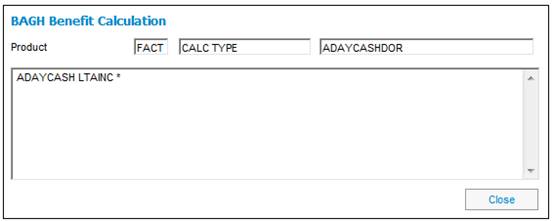
The salary will be averaged at LRD only, and will be applied to the accrual up to NRD (no accrual after NRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from DOE to NRD (which, in this example, is the only accrual).
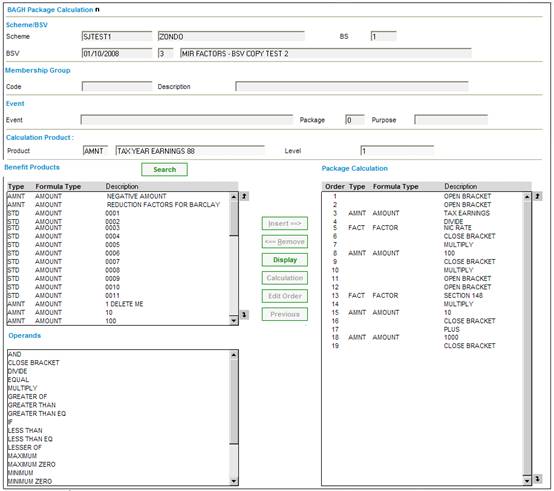
The salary will be averaged at NRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from DOE to NRD (and not to the accrual from NRD to LRD).
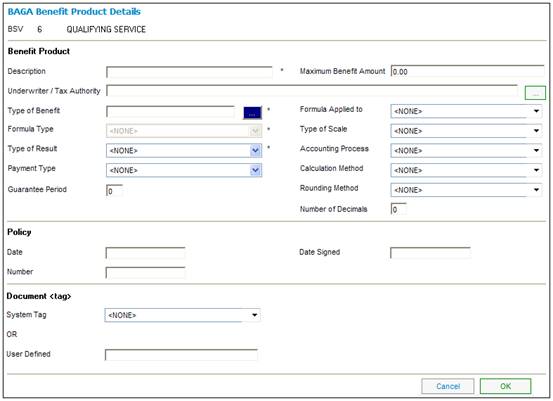
The salary will be averaged at NRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the full accrual from DOE to LRD.
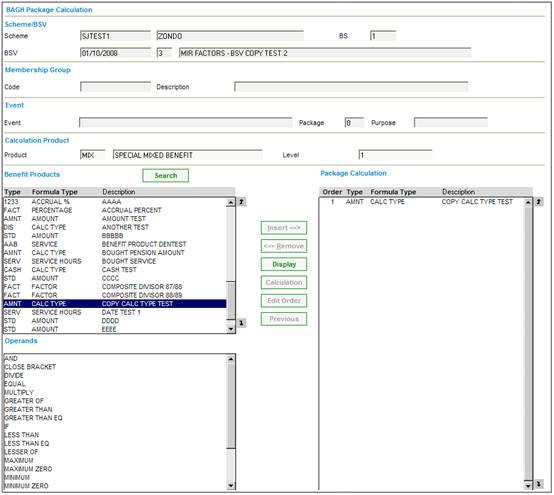
The salary will be averaged at NRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from NRD to LRD (and not to the accrual from DOE to NRD).

The salary will be averaged at LRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from DOE to NRD (and not to the accrual from NRD to LRD).

The salary will be averaged at LRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the full accrual from DOE to LRD.
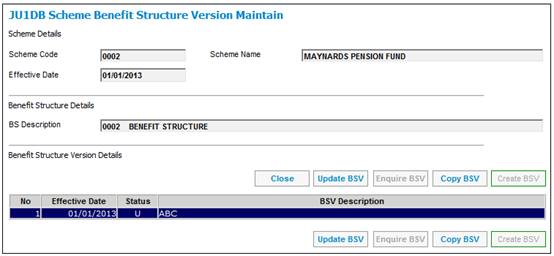
The salary will be averaged at LRD only, and will be applied to the full accrual (from DOE to LRD).
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from NRD to LRD (and not to the accrual from DOE to NRD).
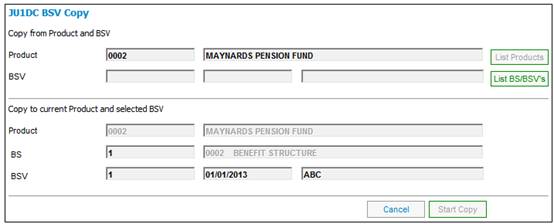
The salary will be averaged at both LRD and NRD, and will be applied respectively to the accrual from NRD to LRD and the accrual from DOE to NRD.
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from DOE to NRD (and not to the accrual from NRD to LRD).
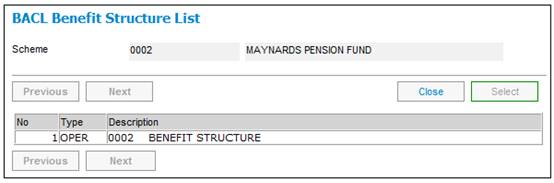
The salary will be averaged at both LRD and NRD, and will be applied respectively to the accrual from NRD to LRD and the accrual from DOE to NRD.
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the full accrual from DOE to LRD.
The salary will be averaged at both LRD and NRD, and will be applied respectively to the accrual from NRD to LRD and the accrual from DOE to NRD.
An increase of 6% pa (based on the period of lateness from NRD to LRD) will be applied to the accrual from NRD to LRD (and not to the accrual from DOE to NRD).